Social Psychology of Emotion
Introduction
Emotions are integral to the human experience, profoundly influencing our thoughts, behaviors, and social interactions. The social psychology of emotion examines how emotions are shaped by and, in turn, shape our social environment. At ivyleagueassignmenthelp.com we help and guide students to explores the origins of emotions, the factors that influence them, and their significant impact on our social lives and mental health.
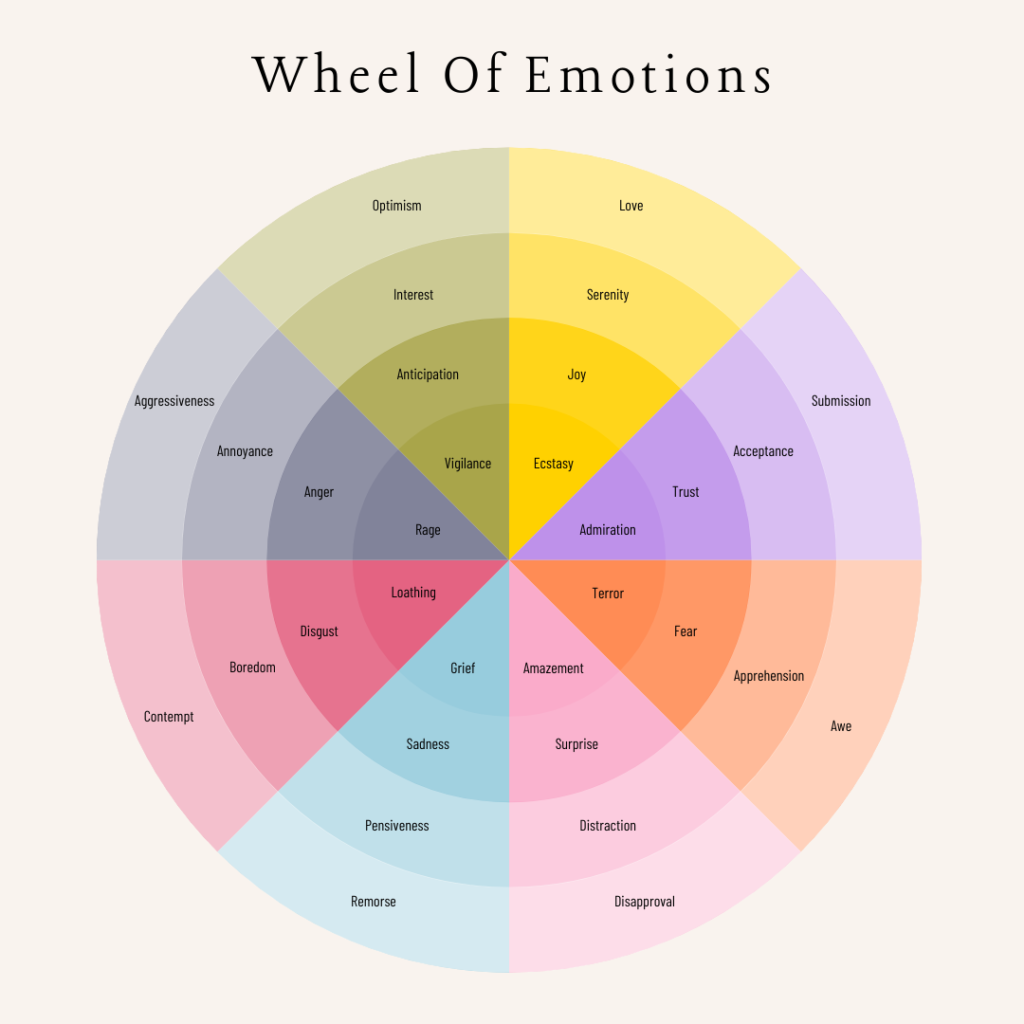
Defining Emotions
Conceptual Framework
- Emotion: A complex psychological state involving an interplay of physiological arousal, cognitive appraisal, and behavioral expression.
- Affect, Mood, and Emotion: Differentiating between these related concepts.
Theories of Emotion
Basic Emotion Theory
- Paul Ekman’s Basic Emotions: Universally recognized emotions such as happiness, sadness, fear, anger, surprise, and disgust.
- Cross-Cultural Studies: Evidence supporting the universality of basic emotions.
James-Lange Theory
- Physiological Basis: Emotions arise from physiological responses to stimuli.
- Sequential Process: The sequence of event, physiological response, and emotional experience.
Cannon-Bard Theory
- Simultaneous Processing: Physiological arousal and emotional experience occur simultaneously.
- Central Nervous System: The role of the brain in processing emotions.
Schachter-Singer Two-Factor Theory
- Cognitive Appraisal: Emotion arises from physiological arousal and cognitive labeling.
- Experiments and Evidence: Supporting studies and real-life applications.
Appraisal Theory
- Cognitive Appraisal: Emotions result from individual interpretations of events.
- Primary and Secondary Appraisal: Evaluating the significance and coping abilities.
Social Constructivist Theory
- Cultural Variability: Emotions are constructed based on cultural norms and socialization.
- Language and Emotion: How language shapes emotional experiences.
Development and Socialization of Emotions
Childhood and Adolescence
- Emotional Development: The emergence and growth of emotional understanding and regulation.
- Socialization Agents: The role of family, peers, and media in shaping emotions.
Adulthood
- Emotional Maturity: Changes in emotional experience and regulation across the lifespan.
- Influence of Life Events: How significant life events shape emotional trajectories.
Cultural Influences on Emotion
Cultural Norms and Display Rules
- Emotional Expression: How culture dictates appropriate emotional expressions.
- Cross-Cultural Differences: Variations in emotional norms across cultures.
Individualism vs. Collectivism
- Emotional Valence: How cultural orientation affects emotional experiences and expression.
- Social Contexts: Differences in emotions within individualistic and collectivistic societies.
Cultural Syndromes
- Cultural-Specific Emotions: Emotions unique to certain cultures, such as Japanese “amae” or German “schadenfreude.”
- Impact on Behavior: How these emotions influence social interactions.
Emotions in Social Interactions
Social Functions of Emotions
- Communication: How emotions convey information to others.
- Social Bonding: The role of emotions in forming and maintaining relationships.
- Regulation of Social Behavior: Using emotions to influence others’ behavior.
Emotion Contagion
- Spread of Emotions: How emotions can be transferred from one person to another.
- Mechanisms: The processes underlying emotional contagion, such as mimicry and empathy.
Interpersonal Relationships
- Role of Emotions: How emotions shape interactions in friendships, family, and romantic relationships.
- Conflict and Resolution: Emotional dynamics in resolving conflicts.
Emotional Intelligence
Components of Emotional Intelligence
- Self-Awareness: Recognizing one’s own emotions.
- Self-Regulation: Managing and controlling emotional responses.
- Social Awareness: Understanding others’ emotions.
- Relationship Management: Using emotional skills to manage interactions.
Importance of Emotional Intelligence
- Personal Success: Correlation with academic, professional, and personal achievements.
- Social Functioning: Enhanced interpersonal skills and social relationships.
Emotion Regulation
Strategies for Emotion Regulation
- Cognitive Reappraisal: Changing the way one thinks about a situation.
- Suppression: Inhibiting the outward expression of emotions.
- Problem-Focused and Emotion-Focused Coping: Addressing the source of stress versus managing emotional responses.
Impact on Mental Health
- Adaptive vs. Maladaptive Strategies: Differentiating between healthy and unhealthy emotion regulation methods.
- Long-Term Effects: How regulation strategies impact overall well-being.
Theories of Emotion
| Theory | Key Concept | Proponents |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Emotion Theory | Universality of basic emotions | Paul Ekman |
| James-Lange Theory | Emotions follow physiological responses | William James, Carl Lange |
| Cannon-Bard Theory | Simultaneous emotion and physiological response | Walter Cannon, Philip Bard |
| Schachter-Singer Two-Factor Theory | Emotion from arousal and cognitive labeling | Stanley Schachter, Jerome Singer |
| Appraisal Theory | Cognitive evaluation leads to emotion | Richard Lazarus |
| Social Constructivist Theory | Emotions are culturally constructed | Various |
Components of Emotional Intelligence
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Self-Awareness | Recognizing and understanding one’s own emotions |
| Self-Regulation | Managing and controlling emotional responses |
| Social Awareness | Recognizing and understanding others’ emotions |
| Relationship Management | Using emotional skills to manage social interactions |
Applications and Implications
Personal Development
- Emotional Awareness: Techniques for increasing self-awareness of emotions.
- Coping Strategies: Developing healthy emotion regulation practices.
Educational Settings
- Social-Emotional Learning (SEL): Integrating emotional intelligence into curricula.
- Bullying Prevention: Using emotional awareness to reduce bullying.
Workplace Dynamics
- Leadership and Emotional Intelligence: The role of emotions in effective leadership.
- Team Cohesion: How emotional intelligence fosters teamwork and collaboration.
Mental Health Interventions
- Therapeutic Approaches: Emotion-focused therapy and its benefits.
- Mindfulness Practices: Using mindfulness to enhance emotional regulation.
Conclusion
The social psychology of emotion provides valuable insights into how emotions are shaped by and influence our social environment. Understanding the origins, development, and regulation of emotions is crucial for improving interpersonal relationships, enhancing emotional intelligence, and promoting mental health. By integrating these concepts into personal development, education, and professional settings, we can foster a more emotionally aware and empathetic society.
FAQs
What is the difference between emotion, mood, and affect?
Emotion is a short-lived, intense response to a specific event. Mood is a longer-lasting, less intense emotional state not tied to a particular event. Affect is a broad term encompassing both emotions and moods, referring to the experience of feeling or emotion.
How do cultural norms influence emotional expression?
Cultural norms dictate what emotions are appropriate to express in different contexts. For example, some cultures may encourage open expression of emotions, while others may promote restraint and control over emotional displays.
What role does emotional intelligence play in personal and professional success?
Emotional intelligence enhances personal and professional success by improving self-awareness, self-regulation, social skills, empathy, and relationship management. These skills contribute to better decision-making, conflict resolution, and overall well-being.
How can individuals improve their emotional regulation skills?
Individuals can improve emotional regulation skills through techniques such as cognitive reappraisal, mindfulness practices, problem-focused and emotion-focused coping strategies, and seeking support from mental health professionals.
How do emotions impact mental health?
Emotions impact mental health by influencing stress levels, coping mechanisms, and overall psychological well-being. Effective emotion regulation and emotional intelligence are crucial for maintaining mental health and preventing emotional disorders.
