Problem-solving is one of those key skills you will need both at home and at work. It is about locating the problems, figuring out what’s wrong, thinking about how to solve them, and then doing it. Problem-solving methods will make decisions more intelligent, generate more creative ideas, and produce better results. We at ivyleagueassignmenthelp.com teach students problem-solving skills and explain to you in great detail how you can master tough situations.
Understanding the Basics of Problem-Solving
Defining Problem-Solving
Problem-solving is a mental process that involves discovering, analyzing, and resolving problems. The goal is to overcome obstacles and find a solution that best resolves the issue.
The Importance of Problem-Solving Skills
You need to have strong problem-solving skills, as this is how you deal with difficult situations successfully and efficiently. They also create better decisions, better connections, and higher output.

Types of Problem-Solving Methods
Analytical Problem-Solving
Analytical problem-solving involves breaking down a problem into smaller, manageable parts and examining each part systematically. It is often used in scientific and technical fields.
Creative Problem-Solving
Creative problem-solving focuses on generating innovative and unconventional solutions. It encourages thinking outside the box and is commonly used in artistic and entrepreneurial contexts.
Steps in the Problem-Solving Process
Identifying the Problem
The first step in problem-solving is to define and understand the problem clearly. This involves gathering information, observing, and pinpointing the root cause.
Generating Possible Solutions
Once the problem is identified, brainstorm possible solutions. Consider all potential options, even those that seem less conventional.
Evaluating and Selecting Solutions
Assess the feasibility, advantages, and disadvantages of each potential solution and select the one that offers the best overall outcome.
Implementing the Solution
Develop a plan to implement the chosen solution. This includes allocating resources, assigning tasks, and setting timelines.
Monitoring and Reviewing
After implementation, monitor the solution’s effectiveness. Make adjustments as necessary and review the process to identify any lessons learned.
Common Problem-Solving Techniques
Brainstorming
Brainstorming is a group activity that encourages open and free-flowing ideas to generate creative solutions. It fosters collaboration and diversity of thought.
Mind Mapping
Mind mapping is a visual technique that helps organize thoughts and ideas around a central problem. It helps in exploring different aspects of the problem and seeing connections between them.
SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis involves evaluating the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats related to a problem. SWOT analysis provides a comprehensive view of the internal and external factors affecting the issue.
Root Cause Analysis
Root cause analysis seeks to identify the fundamental cause of a problem. By addressing the root cause, it aims to prevent the problem from recurring.
Problem-Solving in Different Contexts
Business Problem-Solving
In business, problem-solving is crucial for improving processes, addressing customer complaints, and driving innovation. Methods like Six Sigma and Lean are often used.
Personal Problem-Solving
Personal problem-solving involves addressing issues in daily life, such as managing time, resolving conflicts, and making important decisions.
Educational Problem-Solving
In education, problem-solving skills are taught to enhance critical thinking and analytical abilities. Techniques like project-based learning and case studies are used.
Tools for Effective Problem-Solving
Fishbone Diagram
A Fishbone Diagram or Ishikawa or cause-and-effect diagram is a graph that can be used to diagnose and delineate a problem’s causes systematically. It is more like a fish’s shell, the problem at the head, the causes running along the spine, divided into big sections of methods, machines, materials, and staff. The technique allows teams to come up with ideas and prioritize cause potential, which in turn can be leveraged to identify the root cause and craft specific solutions.

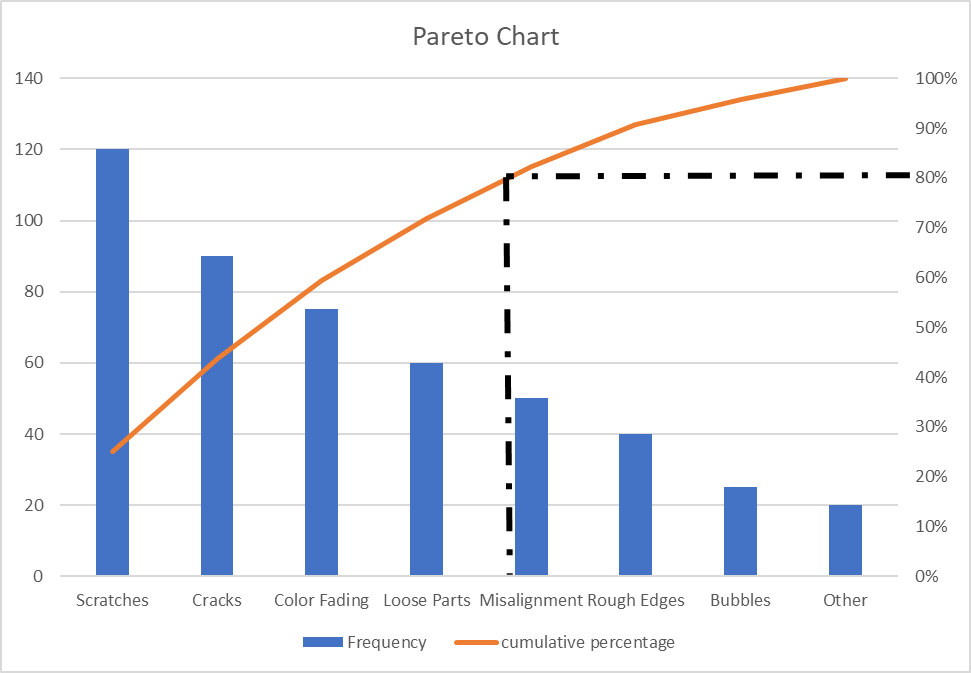
Pareto Chart
A Pareto chart highlights the most significant factors in a problem, helping prioritize which issues to address first. A Pareto Chart is a type of bar graph that represents the principle that roughly 80% of problems are caused by 20% of the causes, highlighting the most significant factors contributing to an issue. Each bar represents a different cause of a problem, arranged in descending order of frequency or impact, with a cumulative percentage line helping to visualize the overall effect of the causes. This tool aids in prioritizing efforts by focusing on the few critical issues that will have the most substantial impact on improving the situation, thereby optimizing resources and time.
A Pareto chart shows the factors with the highest impact on a problem and which issues to tackle first. A Pareto Chart is a bar graph, which is a diagram representing the rule that about 80 percent of problems are attributed to 20 percent of causes, where it highlights the most significant cause for a problem. Each bar is a separate cause of a problem and is descending from commonity/impact and a percentage line in total helps you to understand the overall effect of the causes. This tool helps to prioritize work, and it’s helpful to identify the specific problems that matter the most and will make the biggest impact in improving things so we save the most time and resources.
| Defect Type | Frequency | cumulative total | percentage |
| Scratches | 120 | 120 | 25% |
| Cracks | 90 | 210 | 44% |
| Color Fading | 75 | 285 | 59% |
| Loose Parts | 60 | 345 | 72% |
| Misalignment | 50 | 395 | 72% |
| Rough Edges | 40 | 435 | 91% |
| Bubbles | 25 | 460 | 96% |
| Other | 20 | 480 | 100% |
Problem-Solving Strategies
Trial and Error
This involves testing various solutions until one works. While it can be time-consuming, it is effective for problems with no clear solution.
Algorithmic Approach
Using a step-by-step procedure or formula to solve a problem, this approach is methodical and precise.
Heuristic Methods
Heuristic strategies are general rules of thumb that simplify decision-making. They are quick but may not always provide the best solution.
Developing Problem-Solving Skills
Critical Thinking
Critical thinking involves analyzing facts to form a judgment. It is essential for evaluating solutions and making informed decisions.
Adaptability
Being adaptable allows you to adjust your approach as new information or challenges arise.
Persistence
Persistence is key to overcoming difficult problems. It involves staying committed to finding a solution despite obstacles.
Common Barriers to Problem-Solving
Cognitive Biases
Cognitive biases can distort thinking and decision-making, leading to flawed solutions. Awareness of these biases is crucial.
Emotional Barriers
Emotions like fear, frustration, and anxiety can impede problem-solving. Managing emotions is essential for clear thinking.
Lack of Resources
Limited time, money, or information can hinder problem-solving efforts. Effective resource management is necessary.
Overcoming Problem-Solving Challenges
Seeking Help
Collaborating with others can provide new perspectives and solutions. Don’t hesitate to seek advice or assistance.
Staying Organized
Keeping track of ideas, solutions, and progress is important. Tools like checklists and planners can help.
Continuous Learning
Stay informed about new problem-solving techniques and tools. Continuous learning enhances your skills and adaptability.
Applying Problem-Solving in Real Life
Case Study: Business Scenario
A company facing declining sales uses SWOT analysis and brainstorming to develop a new marketing strategy, leading to increased customer engagement and revenue.
Case Study: Personal Scenario
An individual struggling with time management uses mind mapping to organize their schedule and prioritize tasks, resulting in improved productivity.
Evaluating Problem-Solving Outcomes
Measuring Success
Set clear criteria for success and measure the outcomes against these benchmarks.
Learning from Failure
Not all solutions will work. Analyzing what went wrong can provide valuable insights for future problem-solving efforts.
Problem-solving is a crucial skill that can be honed through practice and application of various techniques. By understanding and implementing different problem-solving methods, you can tackle challenges more effectively and achieve better outcomes in both personal and professional settings. Keep learning and adapting, and you’ll find that your problem-solving abilities will continue to improve over time.
FAQ’s
The main steps are identifying the problem, generating possible solutions, evaluating and selecting solutions, implementing the solution, and monitoring and reviewing.
Brainstorming encourages open and creative thinking, allowing for a wide range of ideas and solutions to be generated and considered.
Analytical problem-solving involves a systematic approach to breaking down and understanding a problem, while creative problem-solving focuses on generating innovative and unconventional solutions.
Critical thinking enhances the ability to analyze facts, evaluate solutions, and make informed decisions, leading to more effective problem-solving.
Cognitive biases are mental shortcuts that can distort thinking and decision-making, often leading to flawed solutions.
Persistence helps overcome obstacles and challenges, ensuring that efforts to find a solution continue despite difficulties.
